Cathy Whitmore, HAIRE’s administrative officer in the Parish of Feock, UK, is a key point of contact for community members. Over the last year, Cathy has spent her time fielding phone calls and organising support for community members throughout the various lockdowns and beyond, and collating points of view from all stakeholders invested in the improvement and development of products and services that aspire to support and enhance the lives of older people – most importantly from older people themselves. HAIRE has offered residents an opportunity to speak up on matters close to their hearts.
The project has provided a sense of purpose, energy, and confidence during a difficult period for those volunteering or working in the community, including businesses, schools and faith groups. The spirit of community has been tested throughout the pandemic; in a previous post discussing the kindness of volunteers at the peak of the covid crisis, 150 volunteers come forward to help their fellow villagers. Because of that, Feock had no difficulties recruiting “HAIRE Enablers” – these are the volunteers who meet with older people to understand their needs and service desires. In fact, there was a 50% over-recruitment of volunteer HAIRE Enablers in the parish, which exceeded all expectations.
A recent interview with volunteer Sue Thomas in Feock featured in our project funder Interreg 2 Seas‘ “Virtual Voyage” online event, which was created for European Cooperation Day on September 21, 2021. Sue joined the project in order to help and support her local community. As part of the HAIRE volunteer preparation process, Sue took part in training sessions designed to provide skills in listening, interviewing, safeguarding and other skills that not only benefit the individual, but the community as a whole. With Interreg showcasing the work of people on the ground all over the 2 Seas area in Europe, we were given a glimpse into Feock volunteers’ achievements. Sue’s interview can be accessed on YouTube here.
Cathy said the project has created a rallying point for key figures in the community – social weavers and influencers. These are people already involved in volunteering, offering and running group activities, and council members, for example – all people who have a vested interested in making the lives of our older people better. To work together on the central theme of healthy ageing will ultimately enable stronger and more linked up solutions. Feock Parish is made up of several communities, and HAIRE has enabled them to envisage themselves as a family of villages within Feock Parish, with similar issues and concerns, rather than separate entities on a scale of importance and status, so that more people can benefit from local initiatives.
HAIRE has given inspiration and motivated fresh personnel to come forward with ideas and offers of support. An intergenerational project has been initiated by a local artist who discovered HAIRE through conversations with the team and they are now putting together plans for a “Memory Shanty Festival.” Older people in the community will share their life stories and unique points of view with schoolchildren, who will work with musicians to produce sea shanties based on real lives in their community. In general, HAIRE has provided people with an opportunity to be creative and innovative – there is “no such thing as a wrong idea”. There is something very powerful in seeing one’s ideas turn into positive action.
The conversations with participants have provided a better understanding of life changes and their impact on a multi-generational level. Ageing impacts us all, not just “older adults”. There is widespread recognition of the danger of a shrinking life world as we age, which puts us at risk of loneliness. Knowing this, it means individuals can start to plan for the future earlier, with the involvement of supporting organisations.
All pilot sites aim to improve the services already in place that have value and link in to them. In Feock, social prescribing’s growing importance and availability means that residents can be signposted to local activities for a range of different reasons, including bereavement, anxiety or loneliness. HAIRE’s volunteers are available “buddy up” with community members depending on their interest – such as swimming, gardening or walking.

The volunteers provide a guiding ‘hand-hold’ to help people discover or return to social activities, developing trust and relationships. The team has created a ‘What’s On’ list and ‘Directory of Groups, Service, and Helplines’ which can be sent to residents, who are later contacted by telephone and given the offer for further advice and support if required in the future. All the activities in the parish are advertised and reviewed on a regular basis in an accessible and inclusive format. They even advertise opportunities in a community phone box.

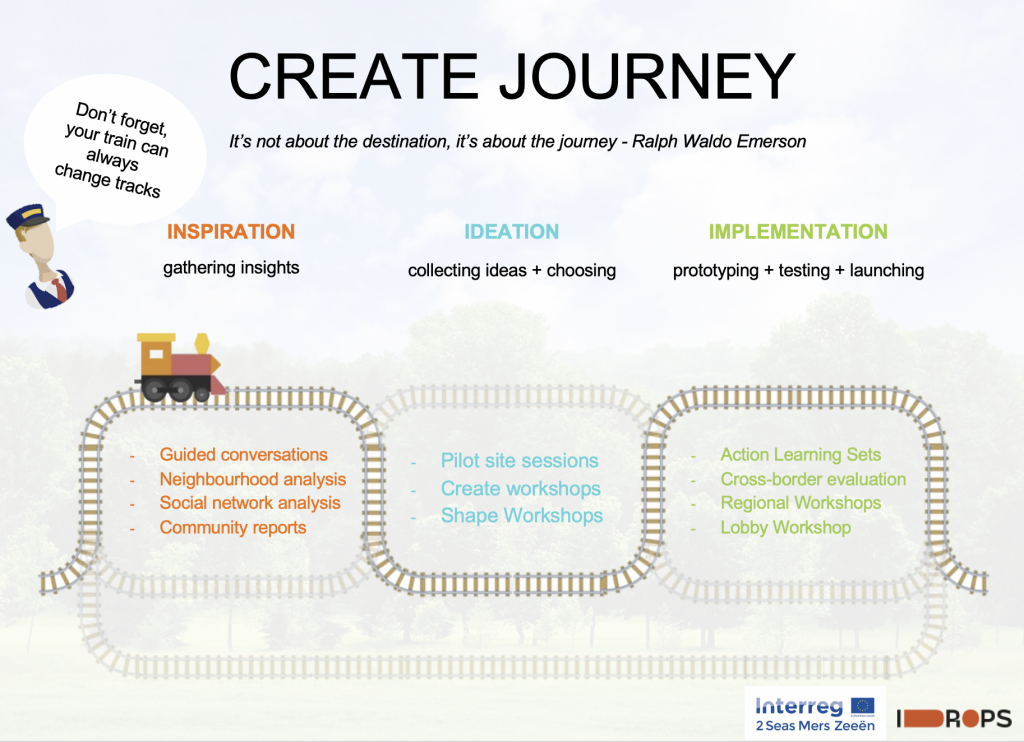
The CREATE workshops held throughout the summer months brought people together in a safe place to share ideas, voice opinions and feel listened to and respected. HAIRE has been able to respond to comments and requests to make quick wins in the short term with opportunities to grow in the long term.

We are all thankful for the work of the amazing volunteers involved in this project. During June’s National Volunteer Month, service users were asked for any comments they would like to pass on to Feock’s volunteers as well as posting on Facebook pages for anyone who would like to thank a member of the community for their support. A beautiful “thank you tree” was put together by a talented resident and used as a backdrop to the CREATE workshop sessions.

Importantly, the work to look at the relevance of services and the creation of new ones won’t just “stop” when the research comes to an end. The communities involved are developing the sorts of skills and opportunities that can really make a difference and can evolve with the times to ensure an organic, thriving culture of listening and learning for positive, age-friendly action with the voices of residents at the fore.
The HAIRE project involves its stakeholders at regular intervals and in different ways throughout the project as we continue to pursue widespread, sustainable system change and to initiate and support innovative models of service delivery. One element of this is to hold regular steering group meetings, such as the Parish of Feock’s HAIRE Action Group Meeting. This took place in September 2021.

 Ha sido una primavera fría y recia para todos los miembros de la comunidad HAIRE: el Reino Unido registró la temperatura más baja en abril desde 1922. Sin embargo, hoy brilla el sol y nos sentimos más esperanzados mientras nos preparamos para el verano y la apertura de nuestras comunidades. A finales de abril, los colaboradores de HAIRE habían elaborado los primeros borradores de los informes comunitarios de nuestras zonas piloto, que combinan la información obtenida en las conversaciones guiadas, los planes de acción y el análisis de los barrios. Nuestros colaboradores se preparan ahora para nuestro próximo gran reto: crear conjuntamente una prestación de servicios innovadora en los lugares piloto y fuera de ellos que responda a los retos identificados en sus zonas. Algunos retos son exclusivos de los centros piloto y otros se derivan de problemas comunes en la Europa rural.
Ha sido una primavera fría y recia para todos los miembros de la comunidad HAIRE: el Reino Unido registró la temperatura más baja en abril desde 1922. Sin embargo, hoy brilla el sol y nos sentimos más esperanzados mientras nos preparamos para el verano y la apertura de nuestras comunidades. A finales de abril, los colaboradores de HAIRE habían elaborado los primeros borradores de los informes comunitarios de nuestras zonas piloto, que combinan la información obtenida en las conversaciones guiadas, los planes de acción y el análisis de los barrios. Nuestros colaboradores se preparan ahora para nuestro próximo gran reto: crear conjuntamente una prestación de servicios innovadora en los lugares piloto y fuera de ellos que responda a los retos identificados en sus zonas. Algunos retos son exclusivos de los centros piloto y otros se derivan de problemas comunes en la Europa rural.