“In the world of social innovation research it is more pertinent than ever to be attentive to change and adapt accordingly to emerging ideas and practices when presented. This has been the experience of the Social innovation Group and our current work on the ANCHOR project.” – Tom Bailey
The University of Exeter’s Social Innovation group (SIG) has now been working on place-based, person-centred issues within the health and social care sector to promote positive change for over 10 years. The primary focus of this multi-disciplinary research group in recent years has been the HAIRE project: Healthy Ageing through Innovation in Rural Europe, which is funded by the Interreg 2Seas European Regional Development Fund. Through the use of a co-designed Guided Conversation (GC) toolkit, HAIRE aimed to reduce loneliness, isolation and improve general wellbeing in the over 60 age group across rural communities in England, Belgium, France and The Netherlands. In terms of practical objectives, the project aimed to develop and test methods that empower and enable participants to:
- Define what support is needed;
- Participate in the design and delivery of services;
- Develop solutions for the individual to reduce loneliness and improve quality of life, health and wellbeing, supported by the voluntary, private and public sectors.
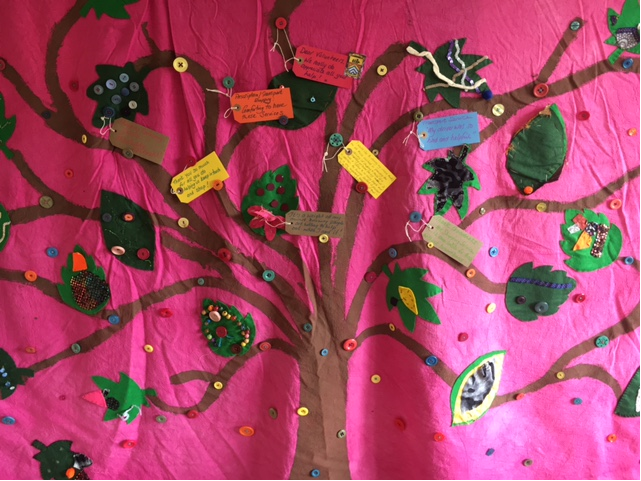
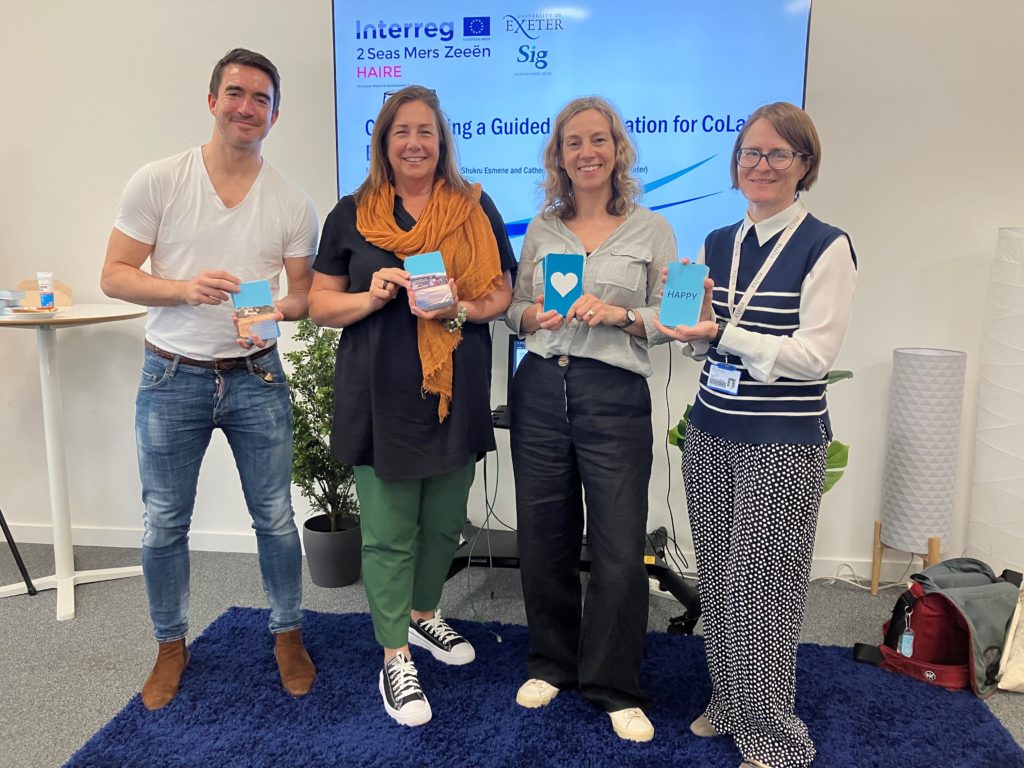
HAIRE’s approach to achieving these objectives included the HAIRE toolkit, which was developed by the University of Exeter with support and consultation from the project partners in adapting the materials to cater to each location site. The toolkit is person-centred and allows for people to reflect on their own needs, interests, and aspirations in order for individualised care and support to be provided. The GC encourages a wide-ranging informal conversation that takes place between volunteers and participants. With the aid of visual and conversational prompts (see Figure 1), the GC fosters an honest and open dialogue between volunteer and participant to identify how the local area, community and the person themselves influence their wellbeing.

Due to the success of the HAIRE project across its eight pilot sites in Northern Europe, a new opportunity to use the same methodology in a wider area arose in Cornwall, England. This was named the ANCHOR project: Supporting Anticipatory Care and Ageing Well in Cornwall. This was funded by the NHS Cornwall Partnership Ageing Well/Urgent Care Response Programme Board as well as the Duchy Health Charity and a UKRI ESRC Impact Accelerator Award.
The aim of this project was to design and develop GCs to be implemented across the Coastal Primary Care Network (PCN) to support communities and anticipate undesired health outcomes. The ‘test and learn’ approach of the project was supported by the assumption that the toolkit would fit into existing work practices without adding to health practitioners’ workloads.
However, during the lifetime of the project there have been two significant innovations to service design and delivery in Cornwall which led the team to re-think how best the GC could fulfil the desired anticipatory care outcomes. These innovations were the emergence of the Community Hub model and a pilot scheme involving Community Health Workers (CHWs). These developments are part of the rapidly changing landscape of service design and delivery involving Cornwall’s voluntary sector (which we will deal with in another article). Understanding and adapting to these changes has been an important part of our work in ANCHOR.
While working in a practical capacity with both organisations and individuals to aid in the delivery of anticipatory care within the new innovation pathways we have also worked in a conceptual capacity to understand anticipatory care as both a philosophy and process of care. As a philosophy, anticipatory care speaks to the working assumption that care (provided by individuals, the community or health services) should enable people to maintain good health and wellbeing for longer. However, for those with chronic conditions, an Anticipatory Care Plan is necessary to precisely identify how an individual should be supported to prevent a deterioration in their condition and unwarranted health outcomes.
The ANCHOR project’s original aims – such as improving the management of long-term conditions, reducing loneliness and isolation, improving general wellbeing and reducing the demand on GP surgeries – are still important but can now be considered long term goals to be achieved while working in the emerging ecosystem of care including through Community Hubs and the CHW programme. Data will continue to be collected on these impacts, but the results will likely be published after the lifetime of the project.
The project is now essentially working to build capacity and skills in the sector that both supports the philosophy and process of anticipatory care. The ANCHOR project’s timeline serves to illustrate that flexibility, resilience and persistence required in the voluntary care sector and in research generally in order to succeed.
Article by Tom Bailey, Research Assistant on the Anchor Project

















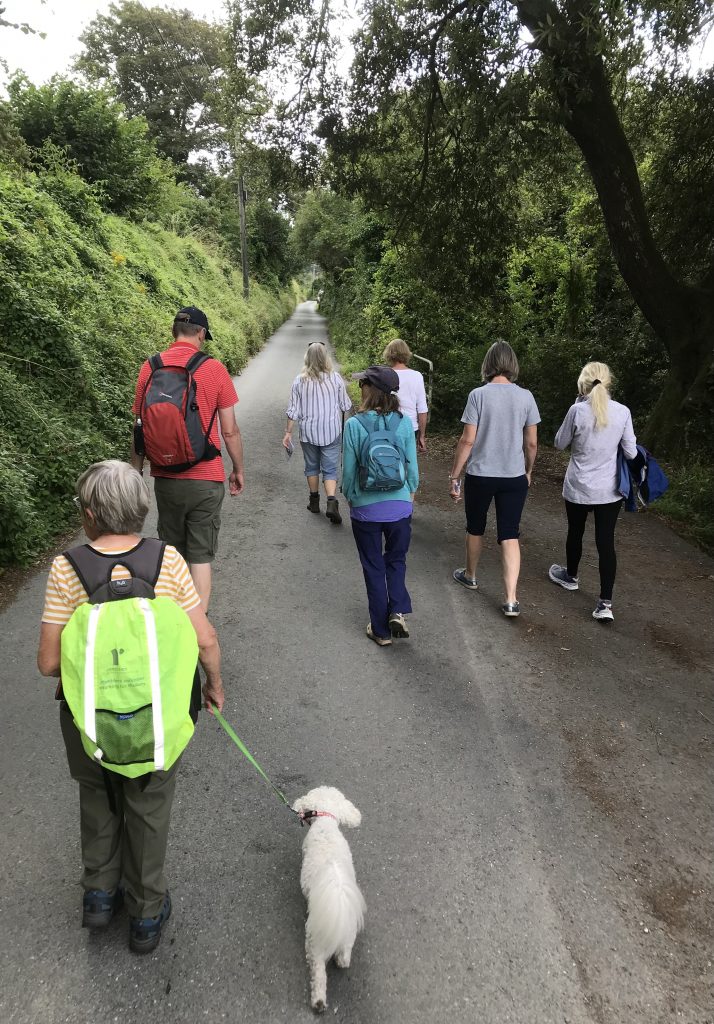
 I turn off the delightfully named Wish Street onto Wish Ward in the direction of a disused factory, a piece of industrial heritage referencing the area’s past. A former bakery, it now houses a pottery. I walk past picturesque redbrick and half shingle houses. The pretty townhouse along a cobbled street with a new Jaguar parked outside tells a story that I’m only too familiar with from Cornwall where the picturesque rural setting can hide great disparities in wealth. Mermaid Street, with its ancient, rounded cobbles, opens up to my left. The Ship Inn – my destination after 7 hours traveling from Cornwall, sits in an attractive riverside location. After dumping my bags, I go for a run along a levee between the river and a nature reserve. It’s a lovely part of the world – startlingly flat compared to Cornwall.
I turn off the delightfully named Wish Street onto Wish Ward in the direction of a disused factory, a piece of industrial heritage referencing the area’s past. A former bakery, it now houses a pottery. I walk past picturesque redbrick and half shingle houses. The pretty townhouse along a cobbled street with a new Jaguar parked outside tells a story that I’m only too familiar with from Cornwall where the picturesque rural setting can hide great disparities in wealth. Mermaid Street, with its ancient, rounded cobbles, opens up to my left. The Ship Inn – my destination after 7 hours traveling from Cornwall, sits in an attractive riverside location. After dumping my bags, I go for a run along a levee between the river and a nature reserve. It’s a lovely part of the world – startlingly flat compared to Cornwall.
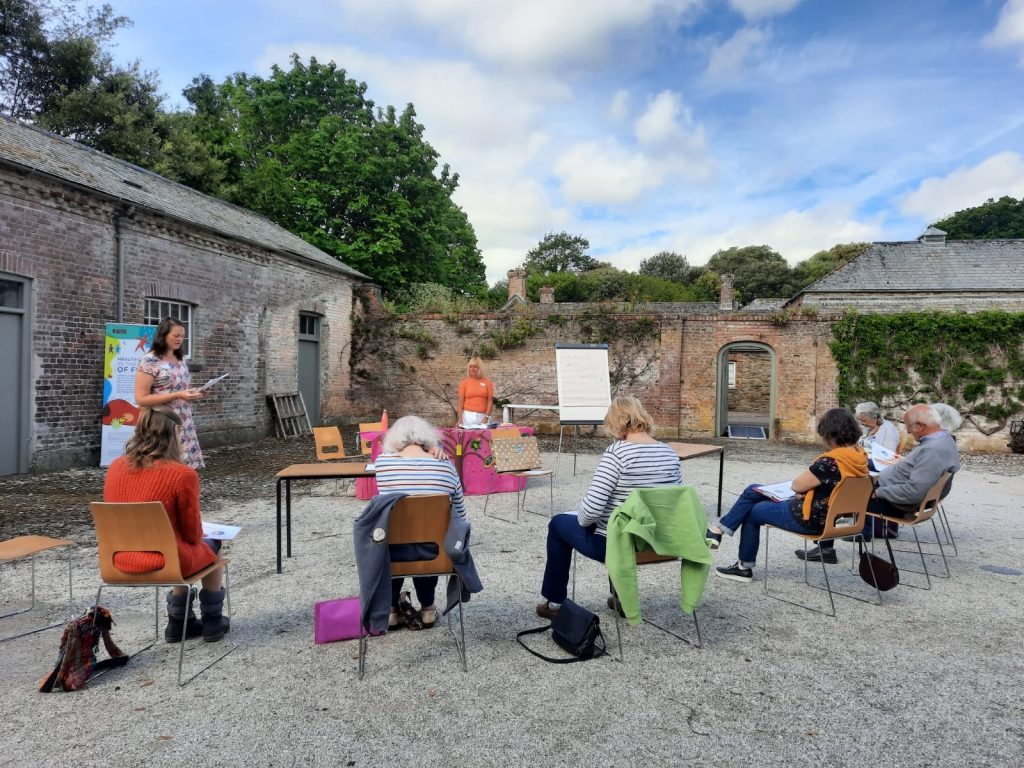
 We have a great meeting, discussing the volunteer experience of using the HAIRE toolkit – especially the Guided Conversation – and the legacy of HAIRE which will be felt through the pilot projects in Age Friendly Rother, now officially a part of the World Health Organisation’s Age Friendly Community programme.
We have a great meeting, discussing the volunteer experience of using the HAIRE toolkit – especially the Guided Conversation – and the legacy of HAIRE which will be felt through the pilot projects in Age Friendly Rother, now officially a part of the World Health Organisation’s Age Friendly Community programme.